New Delhi: Scientists are worried about the emergence of a rare infection in the world battling Kovid, named Monkeypox. Although no case of infection has been reported in India so far, people in Britain, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and America have been found infected with it. Canada, Australia, and France are investigating possible infections of the disease, which can have a fatality rate of 10 percent. In all, there have been over 100 suspected and confirmed cases of monkeypox.
What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare viral infection similar to human smallpox. It was first detected in 1958 in monkeys kept for research. The first case of infection with monkeypox was recorded in 1970. The disease occurs mainly in tropical rainforest regions of Central and West Africa and occasionally spreads to other regions.
Dr. Monalisa Sahu, Consultant on Infectious Diseases, Yashoda Hospital, Hyderabad said, “Monkeypox is a rare zoonotic disease caused by infection with monkeypox virus. The monkeypox virus belongs to the family Poxviridae, which also includes the viruses that cause chickenpox and smallpox.
“Outside Africa, there have been cases of monkeypox in America, Europe, Singapore, UK, and these cases have been linked to international travel and transfer of diseased monkeys from one place to another,” Sahu told PTI. Has gone.”
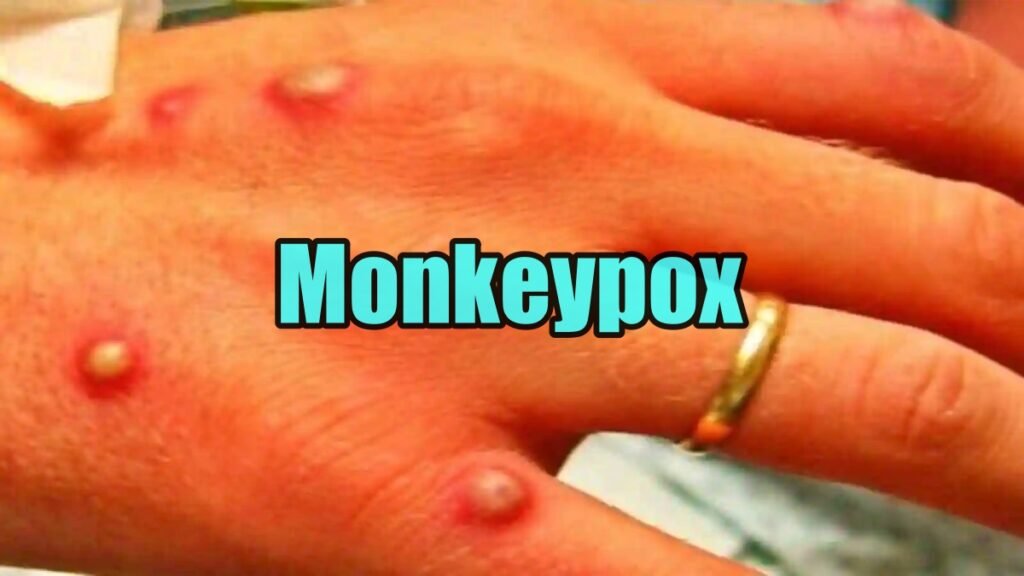
Symptoms of illness According to the World Health Organization (WHO), monkeypox usually presents with fever, rash, and lumps and can lead to a variety of medical complications. Symptoms usually appear for two to four weeks, and go away on their own. Cases can also be serious. In recent times, the proportion of mortality has been around 3-6 percent, but it can be as high as 10 percent. No cause of death has been reported during the current spread of the infection.
How is the infection spread?
Monkeypox is spread to humans through close contact with an infected person or animal, or through material contaminated with the virus. It is believed to be transmitted by animals such as rats, mice, and squirrels. The disease is spread through wounds, body fluids, respiratory droplets, and contaminated material such as bedding.
This virus is less contagious than smallpox and causes less severe illness. Health officials say some of these infections can be transmitted through sexual contact. The WHO said it was also investigating a number of cases involving gay or bisexual people.