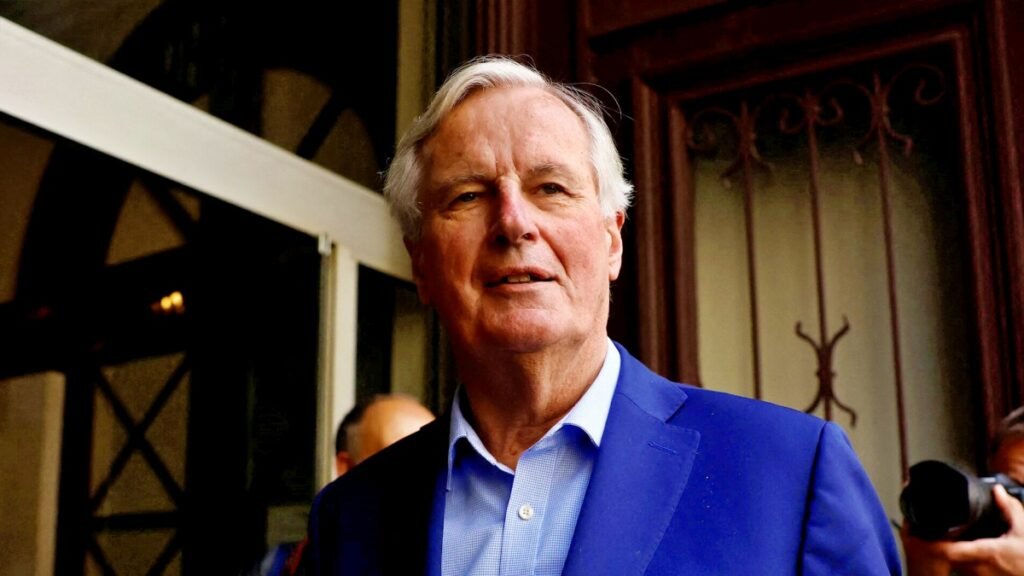
Paris: In a groundbreaking moment for French politics, the government of Prime Minister Michel Barnier collapsed on Wednesday, just three months after its formation. A no-confidence motion tabled by the opposition passed in Parliament, forcing Barnier and his cabinet to tender their resignations to President Emmanuel Macron. This marks the first time in France’s 62-year Fifth Republic history that a Prime Minister has been ousted by a no-confidence vote.
Opposition Motion Secures Overwhelming Support
The no-confidence motion, led by the left-wing coalition The New Popular Front (NFP), gained significant traction, receiving 331 votes in favor, well above the required 288. The motion was fueled by widespread discontent over the recently proposed social security budget, which aimed to increase taxes and cut public spending.
Barnier’s minority government, formed in September after the general elections in July failed to produce a clear majority, was unable to navigate the turbulent political waters.
Social Security Budget Sparks Political Turmoil
The downfall of Barnier’s government can largely be attributed to the controversial social security budget. The budget’s provisions for tax hikes and spending cuts faced backlash across the political spectrum. The government’s decision to bypass a parliamentary vote on the budget further enraged opposition parties, uniting them to bring down the government.
Implications for Macron’s Presidency
The political instability resulting from Barnier’s resignation poses significant challenges for President Macron, both domestically and internationally. Critics are questioning Macron’s strategic missteps, particularly his decision to appoint Barnier, a 73-year-old veteran politician and former EU Brexit negotiator, who now holds the record as France’s shortest-serving Prime Minister.
The Road Ahead: A New Prime Minister Amid Uncertainty
Under the French Constitution, Macron must now nominate a new Prime Minister to form a government. With elections held as recently as July 2024, no new elections can occur until July 2025, leaving Macron to navigate this political crisis within existing constraints.

Growing Concerns Over France’s Stability
The collapse of Barnier’s government signals potential political instability in France, a situation that could impact its role on the global stage. Macron faces the daunting task of uniting a fractured Parliament to avoid further governance crises while ensuring that France’s domestic and international policies remain on course.
As the search for a new Prime Minister begins, all eyes are on Macron’s next move, which could shape the country’s political future and his own legacy as President.