
Key Points:
- 17% of Indians now have diabetes, affecting one in six people
- Average diagnosis age has dropped from late 40s to early 30s
- 17.2% of individuals under 40 have young-onset type 2 diabetes
- Males (10.6%) more affected than females (6.5%) in under-40 age group
- India has 89.8 million adults with diabetes, projected to reach 156.7 million by 2050
- Gen Z showing decline across all wellness pillars
- Teenagers aged 15-16 now showing early signs of obesity and insulin resistance
- Physical inactivity, obesity, stress, and poor diet are primary causes
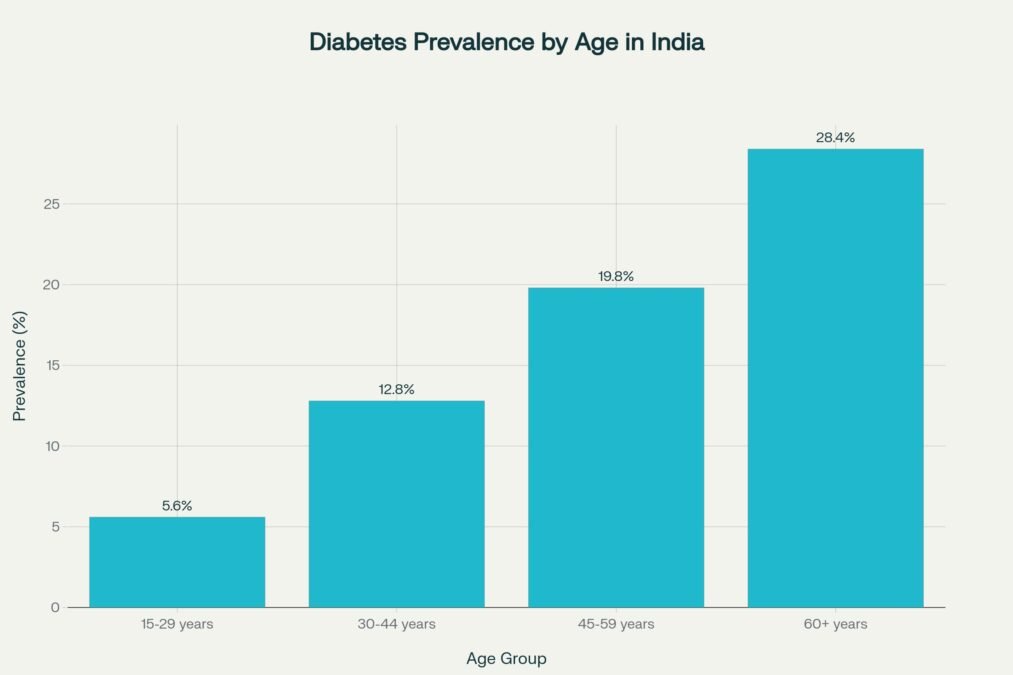
The prevalence of diseases like cancer and diabetes is increasing at an alarming rate worldwide, with India witnessing a particularly concerning surge in diabetes cases among young people. Previously confined to older adults, diabetes is now affecting individuals in their 20s and even teenagers aged 15-16, who are showing early signs of obesity and insulin resistance. According to ICICI Lombard’s India Wellness Index 2025, released on World Diabetes Day, 17% of Indians now report having diabetes, meaning one in six Indians is affected by this chronic condition.
The experts note that the average age of diabetes diagnosis has slipped dramatically from the late forties to the early thirties, driven by long work hours, erratic routines, poor eating habits, and chronic stress. A 2025 study found that 17.2% of individuals under 40 in India have young-onset type 2 diabetes, with a higher prevalence in males (10.6%) than females (6.5%). Currently, India has 89.8 million adults living with diabetes, and this number is projected to reach a staggering 156.7 million by 2050.
Understanding the Causes Behind Youth Diabetes
Health experts emphasize that diabetes in young people stems from a deteriorating lifestyle, chronic stress, and persistent fatigue. Several critical factors are responsible for this alarming increase among younger populations, requiring immediate attention and intervention.
Physical Inactivity and Screen Time
Young people today struggle to maintain proper physical activity due to demanding work schedules, laziness, or lack of motivation. Excessive screen time, whether for work or entertainment, has led to increasingly sedentary lifestyles that significantly elevate diabetes risk. Gen Z, in particular, is showing declines across all wellness pillars, including physical health, with Tier-1 Gen Zs identified as the most vulnerable group.
Obesity Epidemic
Obesity or excess weight stands as a major contributor to diabetes in young people and children. Excess fat tissue increases the body’s resistance to insulin, making it harder for cells to utilize glucose effectively. Teenagers aged 15-16 are now showing early signs of obesity and insulin resistance, indicating that the problem begins even earlier than previously thought.
Genetic Predisposition
Many individuals may develop diabetes due to genetic factors inherited from their family history. However, genetics alone cannot explain the dramatic surge in cases, as environmental and lifestyle factors play equally significant roles in disease manifestation.
Unhealthy Dietary Patterns
An unhealthy diet is a substantial contributing factor to the diabetes epidemic among youth. Consuming fatty foods, excessively processed items, sugary beverages, and fast foods leads to weight gain and impaired glucose metabolism. The corporate lifestyle, with irregular meal timings and reliance on quick, unhealthy food options, has particularly affected millennials and young professionals.
Environmental Factors
Air pollution and constant exposure to certain harmful chemicals can reduce insulin sensitivity, thereby increasing disease risk. Urban environments, where pollution levels are typically higher, see greater diabetes prevalence among young residents.
Chronic Stress
Prolonged stress increases cortisol levels in the body, which directly affects blood sugar control. According to the 2025 Wellness Index, one in three Indians reports high daily stress, with 41% experiencing constant tiredness. Millennials and corporate women report the highest vulnerability to stress-related health issues, with young Indians reporting an average of 1.3 depression symptoms.
Serious Health Consequences
Experts warn that uncontrolled diabetes for even five years can place patients in a high-risk category for heart disease, stroke, and kidney complications. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body’s cells fail to respond properly to insulin, leading to persistently high blood sugar levels. There is currently no cure for diabetes, making prevention and management through lifestyle changes absolutely critical.
Five Essential Lifestyle Changes to Control Diabetes
Controlling diabetes requires comprehensive lifestyle modifications that address multiple aspects of daily living. Here are five evidence-based strategies for managing and preventing diabetes in young people.
Regular Physical Activity
To effectively control diabetes, engage in at least 60 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, manage weight, and reduce overall disease risk. Activities can include brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or any form of movement that elevates heart rate and promotes calorie burning.
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Following a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats significantly reduces diabetes risk. Avoid fatty foods, processed items, sugary drinks, and fast foods that contribute to weight gain and glucose dysregulation. Focus on portion control, regular meal timings, and adequate hydration to support metabolic health.
Stress Management Techniques
To reduce stress and its impact on blood sugar levels, practice yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises regularly. These techniques not only improve mental health but also enhance overall wellness by lowering cortisol levels and promoting relaxation. Millennials and corporate women, who show the highest stress vulnerability, should particularly prioritize these practices.
Comprehensive Lifestyle Modifications
Managing diabetes requires attention to multiple factors simultaneously, including healthy eating, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and effective stress management. Avoid tobacco use and limit alcohol consumption, as these habits can worsen blood sugar control. Maintaining consistent routines for sleep, meals, and physical activity helps stabilize metabolism and improve disease outcomes.
Regular Health Monitoring
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels through consistent monitoring is essential for diabetes management. Regular checks of blood glucose levels, HbA1c (which reflects average blood sugar over three months), and other health indicators help track progress and adjust treatment strategies. Early detection through screening allows for timely intervention, preventing complications and improving long-term health outcomes.
Call for Action
With Indians without heart or diabetes conditions scoring 79 on the Wellness Index compared to just 70 for those living with such ailments, the impact of these diseases on overall quality of life is undeniable. The dramatic rise in youth diabetes demands immediate action from individuals, families, healthcare providers, and policymakers to reverse this concerning trend through education, prevention, and early intervention strategies.
















































